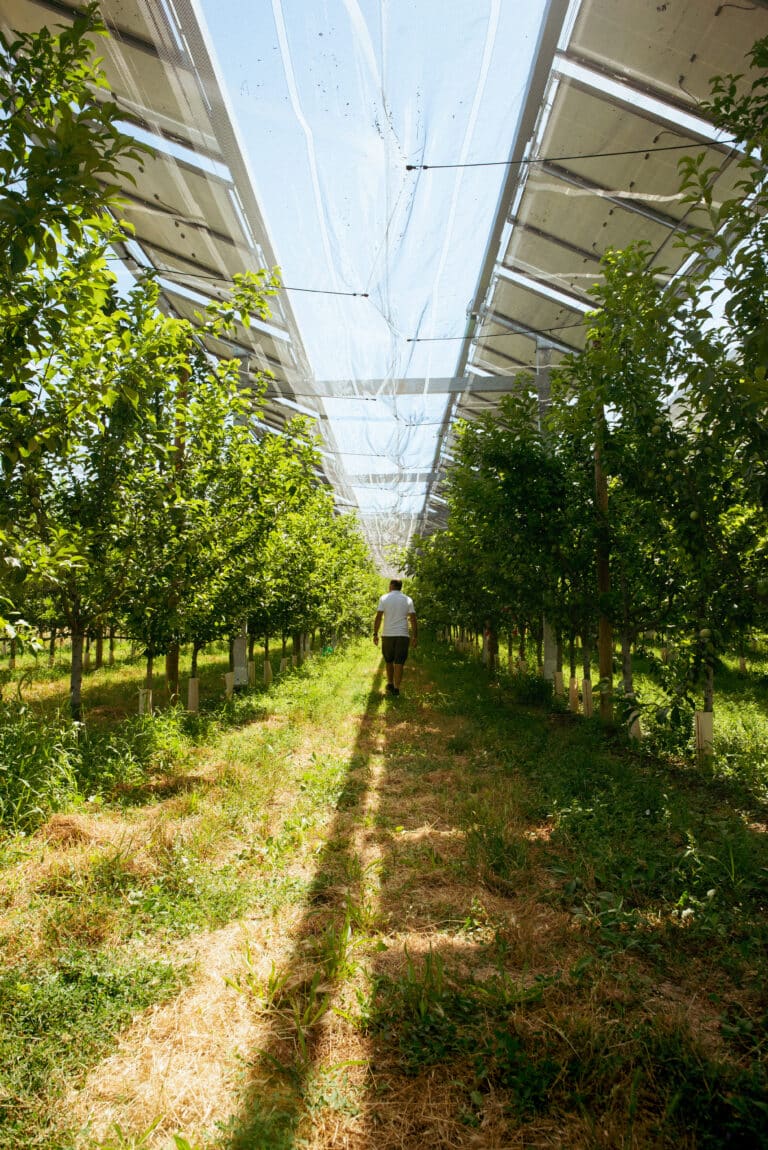
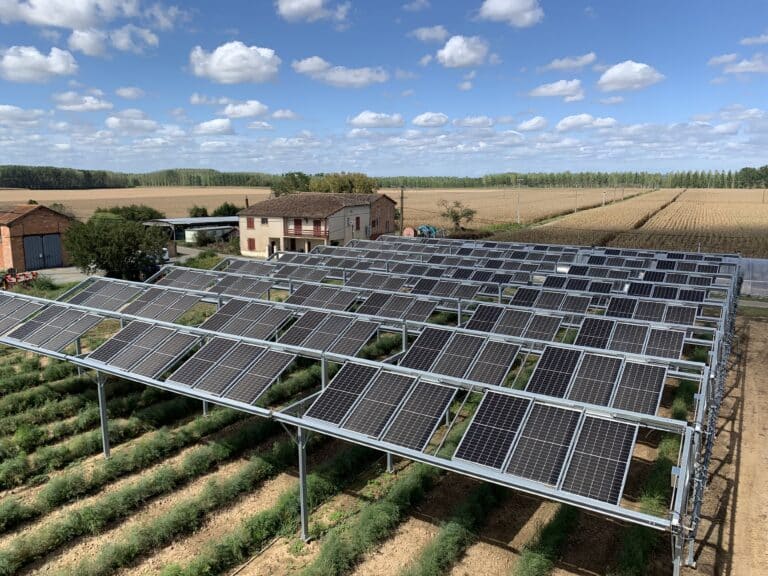
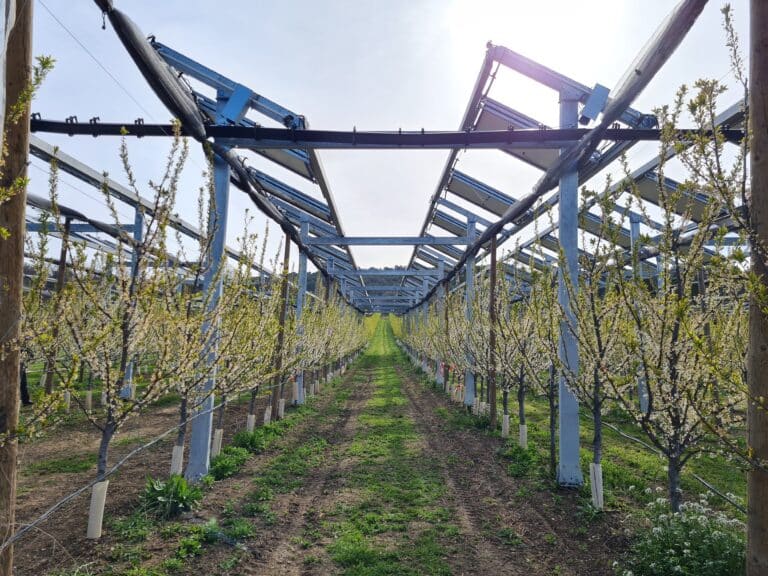
Agrivoltaics is the combination of significant agricultural production and renewable energy production on the same plot of land, with the aim of achieving optimum synergy between the two. To achieve this goal, agrivoltaic installations, also known as agricultural photovoltaic shading systems, are set up on a given plot of land.
There are several types of agricultural photovoltaic shading systems to suit different types of farming (arable farming, viticulture, cattle or sheep rearing, etc.) and needs. In this article, we'll explain what agricultural photovoltaic shade systems are, the benefits they bring and how to integrate them into your farming operations!
What is an agricultural photovoltaic shade?
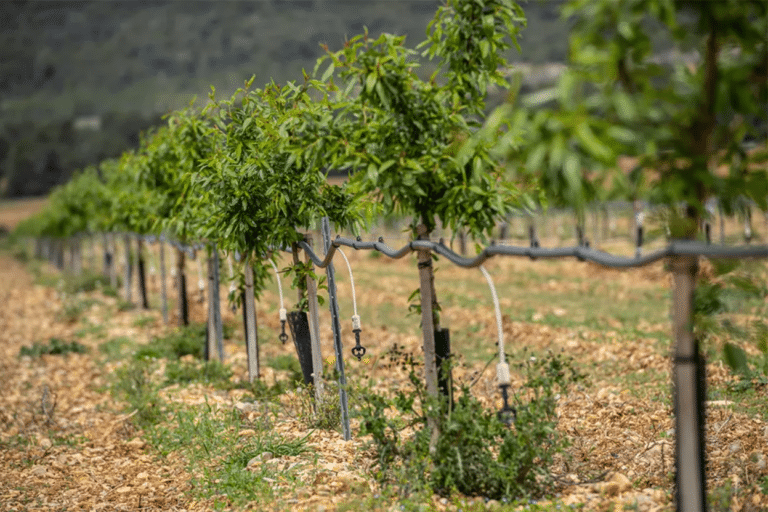
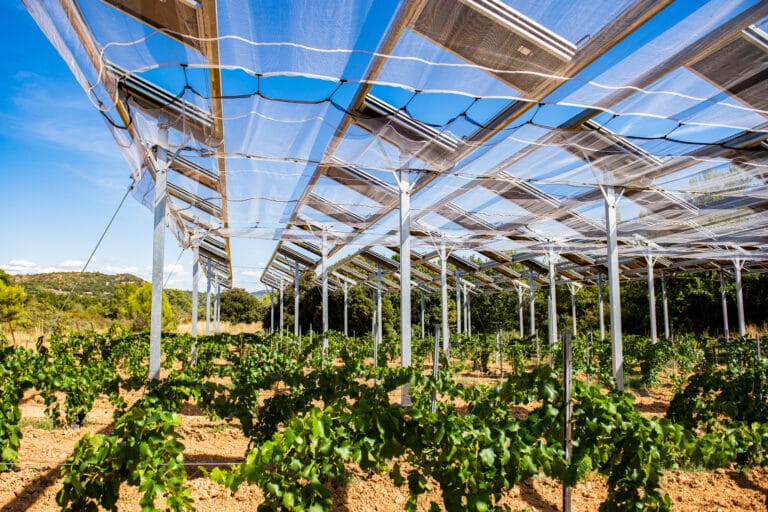
An agricultural photovoltaic shade is a solar energy solar energy production systemspecifically designed to adapt, protect and even enhance agricultural production on a plot of land. There are a number of different types: lvertical bifacial panelsfixed raised panelsrotative shading systems eand trackers.
Among these various installations, which we describe in greater detail on our websitewe can distinguish two main categories: fixed technologies (where the panels are immobile) and controlled technologies (where the panels are controlled by an algorithm that integrates real-time microclimate data from sensors on the plot - their movement modifies the shadows cast on the ground and on the crops).
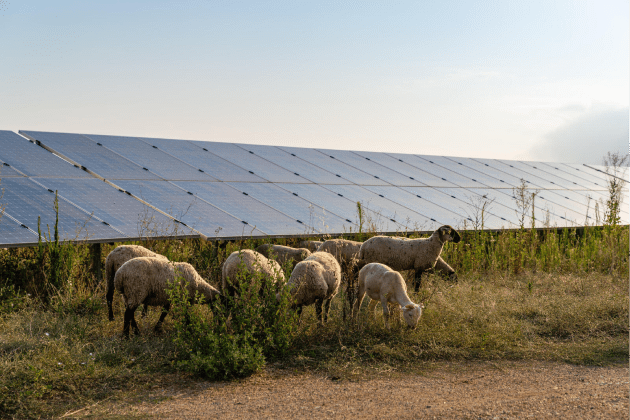

Whereasconventional" solar systems are installed with l'sole purpose to produce solar-generated electricity, lagricultural photovoltaic shading systems, on the other hand, designed and installed with the aim of preserving agricultural production as their main activity by offering real services to crops. Energy production comes second.
The advantages of agricultural photovoltaic shade systems
Agricultural photovoltaic shading systems offer a number of advantages to the farm where they are installeds locatednt.
Agronomic benefits for crops
First and foremost, they offer protection for crops and livestock by providing a range of agronomic benefits. When the right amount of shade is provided by agrivoltaic installations, they protect crops from the stresses they face (thermal, hydric and oxidative stress) extreme weather conditions. We can cite the following agronomic benefits in particular:
- Adapting shade to the plant's needs in order to reduce the risk of burns and limit evapotranspiration.
- The creation of a microclimate favorable to their growth by adapting the temperature and humidity in the soil and at plant level. In particular, this ensures sufficient cold accumulation during dormancy for perennial crops, or a reduction in reduce heat stress during hot spells.
- L'mproving animal well-beingwith livestock benefiting from greater thermal comfort under shade.
The shades also provide protection against hail, by installing anti-hail netting, which is possible on some controlled agricultural photovoltaic shades.
Agrivoltaic installations can help improve soil quality by preserving its biodiversity. We explain why the issue of biodiversity is central and how we assess its preservation in the context of agrivoltaic projects in this article on the Ombrea blog.
The agronomic benefits mentioned above will help the farm to stabilize or even increase yields.
Power generation
The installation of agricultural photovoltaic shading systems will also enable a new activity to be set up on the farm: the production of renewable energy. Although farming will remain the main activity, this complementary activity will bring about a income diversification for the farmerIt will also help ensure the long-term future of the farm.
Did you know? The electricity generated by the solar panels is transported from the site to a delivery or connection station via an underground cable. The electricity is then sent to the nearest source substation, from where it is distributed on the power grid to end consumers.
"10 questions about agrivoltaics - The new Ombrea white paper!
Case studies and testimonials
To study the impact of our agricultural photovoltaic shading systems on crops, we have set up 13 demonstrators throughout France.
Among these, our Channay demonstrator, inaugurated in October 2021, was built to test the effect of our vertical bifacial panels on different cereals (wheat, barley, lentils lentils, alfalfa...). After a year of observation, in 2023, we were able to observe a yield increase of 19% for spring wheat, 10.4% for barley and 17.1% for lentils. "We are increasingly exposed to drought, with episodes of wind and frost causing significant damage to our crops. [...] Thanks to the photovoltaic panels, the crops are better protected with more shade, less wind... In short, the coexistence of these two activities allows us to have a more sustainable agricultural system." explains Jean-Philippe Delacre, farmer at the Channay site.
Our Rians demonstrator, to be inaugurated in 2020, is located in the Var département (83). It consists of a plot of vines protected by translational shades, the height of which is adapted to agricultural machinery. We were able to observe a higher yield under shade in terms of number of bunches, bunch weight and weight per vine, as well as a 5-9 day delay in harvesting under shade and a one-year advance in the date of the first harvest for the protected plot.
"The grapes are ripening like they used to. The vines are finishing their cycle quite normally, with no heat stroke either on the leaves or on the bunches," said Gauthier Hugues, a farmer in Rians.
Installing photovoltaic shade systems on your farm: how does it work?
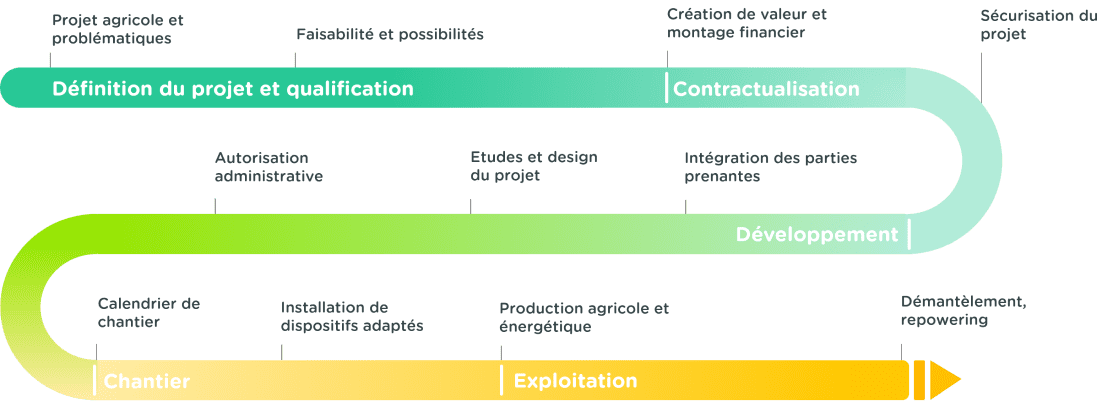
The development of an agrivoltaic project takes between 4 and 6 years and is divided into 3 phases.
- The first phasecorresponds to the definition and qualification of the project. This allows us to validate the solution adapted to the specific needs of each operation, as well as its feasibility. For this, at Ombrea, we rely on numerical tools developed in-house that enable us to simulate variations in indicators of interest on a plot equipped with an agrivoltaic system, in comparison with a reference area.
- The second phase covers the various permit applications required to build an agrivoltaic project. Contractualization and project development can take between 2 and 4 years.
- Finally, the third phase corresponds to the completion of the project and its operation. The operating phase is governed by the law on the acceleration of renewable energy production (or APER law) and has a maximum duration of 40 years. During this period, ADEME will monitor agricultural and energy production on an annual basis.
Frequently asked questions (FAQ)
What types of crops can benefit from agricultural photovoltaic shade systems?
As agrivoltaics is a fast-growing field, the extent of its possibilities has yet to be discovered. However, an agrivoltaic system is designed to be adapted to the needs of all crops and livestock to bring them agronomic benefits.
What is the return on investment for an agricultural photovoltaic shading system?
The installation of agricultural photovoltaic shading systems is governed by the APER lawlaw, stipulating that they must generate a sustainable income for the farmer while providing agronomic services to the plot.
Do agricultural photovoltaic shading systems affect plant growth?
Agricultural photovoltaic shade systems must not have a negative impact on plants and animals. At Ombrea, in order to accurately assess the effects on crops of each agrivoltaic project we undertake, we rely on our in-house developed digital tools. These tools enable us to simulate variations in key indicators (temperature, humidity, irradiance) on a plot equipped with an agrivoltaic system, compared with an unequipped reference area.
What are the main constraints on the installation of agricultural photovoltaic shading systems?
The main constraint for the installation of agricultural photovoltaic shading systems is the match between the organization of the agrivoltaic site and the agricultural activity, in particular the compatibility between its design and agricultural machinery.
Our knowledge of farming methods and machinery, and our close collaboration with farmers throughout the development of a project, enable us to propose solutions that optimize the synergy between energy production and agricultural production.
Agricultural photovoltaic shading systems bring many advantages to agriculture, generating agronomic benefits, significant income and sustainable energy production! sustainable energy production! Would you like to find out more? The white paper "L'agrivoltaics in 10 questions" is available to download in just one click!