L'agrivolatism refers to a practice combining agriculture and photovoltaics. Its objective is to combine solar energy production with agricultural production for create synergies. Opportunities for the agricultural sector, agronomic benefits, risks and precautions to be taken: this topic raises many questions for professionals in the sector. which we will answer in this article.
Origins and definition of agrivoltaics
First introduced in Japan in the 1980sagrivoltaics then developed in Asia, mainly in rice growing and market gardening. However, it it take 30 years to see the emergence of the first agrivoltaic power plants of significant size. The system's benefits for protected cropsected leads tont in much of the world.
Contributing to food and energy sovereignty, theagrivoltaics is an opportunity for the agricultural and energy transitions. In order to respond jointly is emerging in France, almost 40 years after it first appeared in Asia.
In order to guarantee the initial objective of agrivoltaics, the law for the Acceleration of Renewable Energies came to define and frame this practice in 2023. Article 54 defines an agrivoltaic installation as "anyelectricity production facility using the sun's radiative energy, whose modules are located on an agricultural plot where they make a lasting contribution to the installation, maintenance or development of agricultural production".
An agrivoltaic installation must provide at least one of the following four services:
- Improving agronomic potential and impact
- Adapting to climate change
- Protection against climatic hazards
- Improving animal welfare
In addition to these criteria, the project must not substantially affect any of the above-mentioned services, or even have a limited impact on two of them. For example, farming must remain the main activity on the site, and the facility must be reversible. The decrees specifying the application of this law are currently being drafted.
Agronomic benefits, but not only
The services and benefits provided byagrivoltaics are not solely agronomic. In fact, thanks to this type of installation, environmental and economic services are alsoservices.
Impacts on the microclimate and climatic hazards;
Installing panels on cultivated and grazed farmland allows us to provide the conditions required for crop development and animal welfare. This is made possible by aligning the microclimate with the needs of crops and animals.
Thanks to the shade created, the plant's temperature and irradiation parameters can be adapted. The orientation, height and type of technology canut also provide protection against wind, water and wind, water and hail. A fence or adapted netting on rearing pens helps reduce predation.
Impacts on soil and biodiversity;
Agrivoltaic agrivoltaic projects projects can also make a positive contribution to soil quality and biodiversity. The planting of grassed strips in particular helps to maintain by providing a habitat for biodiversity.
Intra-plot planting reduces the distance the beneficials have to travel between their habitat and their prey. Similarly, the grassed strip will be a flowering zone to maintain pollinator populations.. By retaining washed-out soil thanks to a well-established root system and allowing water to infiltrate the soil, these surfaces help to reduce the risk of erosion.
Societal and territorial impacts ;
Agrivoltaic projects, like all renewable energy projects, are first and foremost local projects. They are developed in conjunction with local stakeholders, with the aim of contributing to local issues through economic spin-offs and accompanying measures.
Download the White Paper on best practices for starting an agrivoltaic business
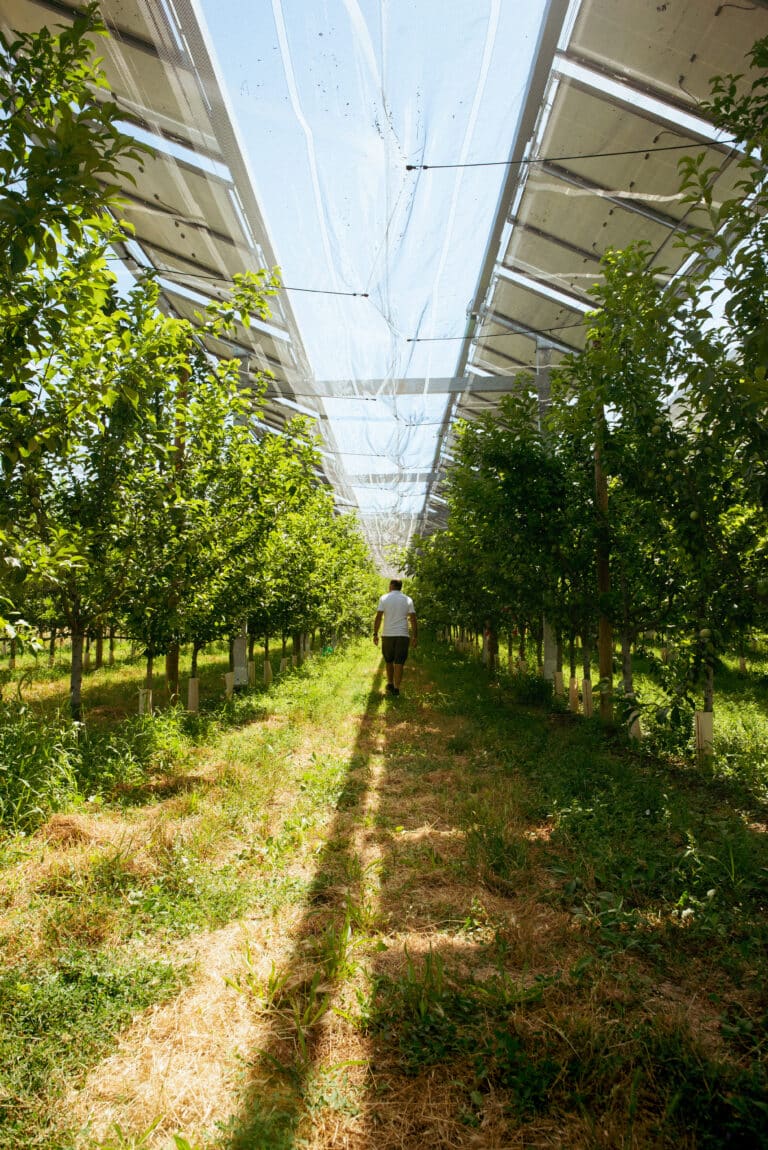
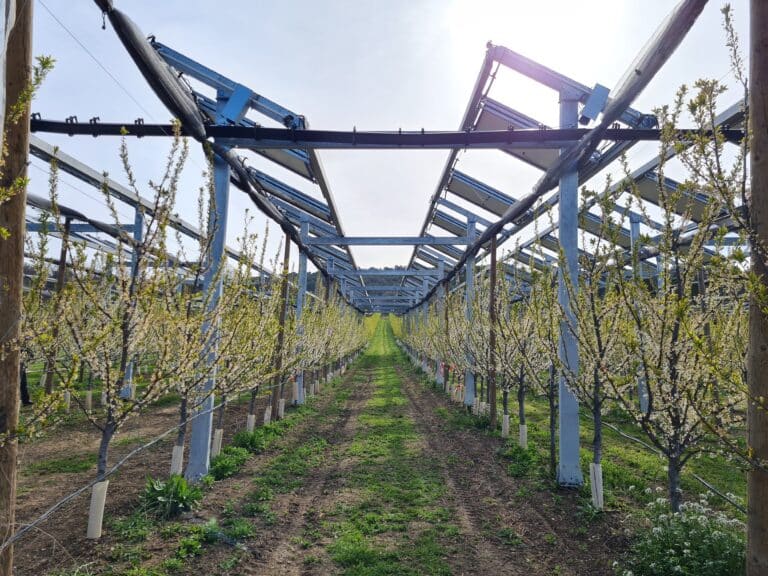
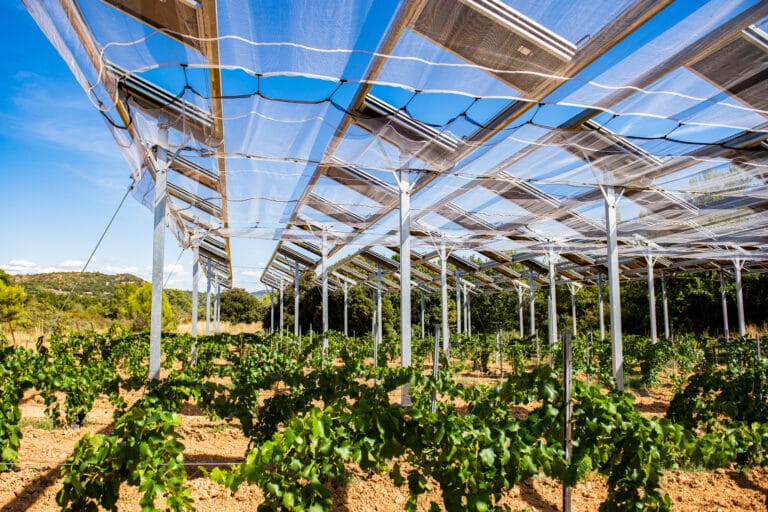
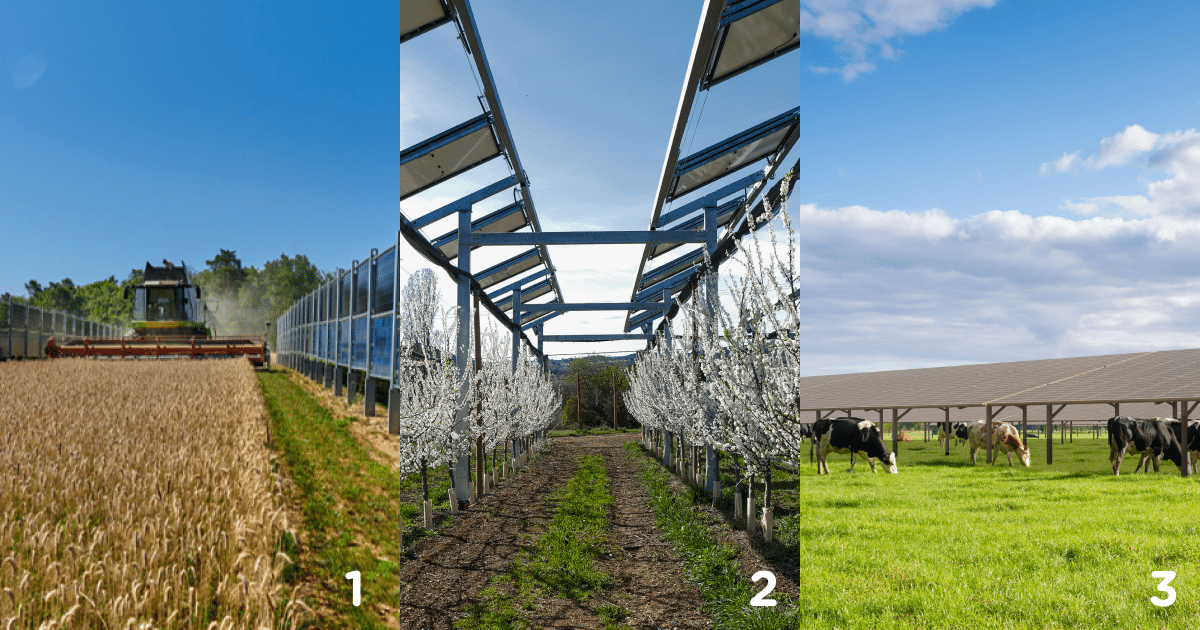
A range of technologies to serve crops
Raised shading systems, controlled modules and vertical panels are just some of the technologies that can be used to provide services to agriculture.
- 1: Vertical panels. This system of fixed vertical bifacial panels, like hedges, creates a windbreak effect that protects crops and limits dehydration. Technology is not the only determinant of the services rendered; every project is different. The height and number of piles, the orientation of the panels and the spacing between rows are all adjustable elements that influence the services rendered by the project.
- 2: Dynamic shading systems and trackers. These systems respond to the needs of crops bydynamically controllingshading, thus creating favorable conditions for plant development.
- 3: Elevated fixed shading systems. In addition to providing shade, this fixed system improves humidity and temperature conditions under the panels.. The result is more even crop growth and better feed for the herd.

Pilot projects and feedback from agrivoltaic sites
Numerous experiments have been carried out to prove the benefits ofagrivoltaics and optimize its development. Here are some of thes benefits observed on our pilot sites.
Microclimate and climatic hazards;
Field crops have been grown on our Le Channay (21 ) site, where vertical panels have been installed since late 2021. Here's an overview of the results observed on the microclimate in 2023:
- 2.5°C reduction in ground temperature in May and June
- 18.5% reduction in wind gust speed
At our site inApt (84), where a controllable agrivoltaic shade has been installed on a plot of plum trees, here are the results observed during the heatwave of August 2023:
- Soil temperature at 55cm reduced by 3°C on average
Quality and performance ;
At our Le Channay (21) site, here's an overview of the results obtained in 2023:
- Lentils +17.8% yield compared to control zone
- BTH (soft winter wheat) +26% yield compared with the control zone
Discover all our pilot sites in our dedicated interactive space!